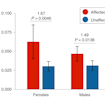
Timothy Yu and colleagues analyzed exome sequencing data to estimate that recessive mutations contribute to approximately 5 percent of all cases of autism, including 10 percent of females.
Highlights of SFARI-funded papers, selected by the SFARI science team.

Timothy Yu and colleagues analyzed exome sequencing data to estimate that recessive mutations contribute to approximately 5 percent of all cases of autism, including 10 percent of females.
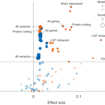
Olga Troyanskaya, Robert Darnell and colleagues applied deep-learning methods to whole-genome sequencing data from SSC families and identified a clear enrichment for de novo noncoding variation in ASD.
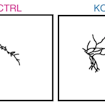
James Ellis and colleagues used a sparse co-culture system for iPSC-derived cortical neurons to assess neuronal connectivity, demonstrating increased connectivity in SHANK2-mediated ASD.

Mark Zylka and colleagues generated single-cell RNA-seq data from wild-type mouse cortex during early development and demonstrated how such a resource can be used to identify putative brain disorder subtypes based on expression profiles.
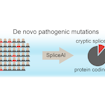
Kyle Kai-How Farh and Stephan Sanders developed a deep-learning method to predict risk mutations that affect mRNA splicing and contribute substantially to neurodevelopmental disorders.
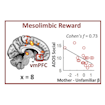
Vinod Menon and colleagues report that a difference in the activation of a voice-processing network comprising reward and salience detection systems is a distinguishing feature of autism.
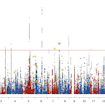
Mark Daly and colleagues report the results of a large genome-wide association meta-analysis of more than 18,000 individuals with ASD, including the newly genotyped Danish iPSYCH cohort.

Evan Eichler and colleagues performed a meta-analysis of de novo mutations from individuals with ASD, intellectual disability or developmental delay and found new risk genes for neurodevelopmental disorders.