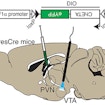
Robert Malenka and colleagues find that oxytocin acts within the ventral tegmental area to increase dopamine reward neurons to reinforce the rewarding aspects of social interactions in mice.
Highlights of SFARI-funded papers, selected by the SFARI science team.

Robert Malenka and colleagues find that oxytocin acts within the ventral tegmental area to increase dopamine reward neurons to reinforce the rewarding aspects of social interactions in mice.
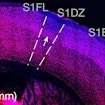
Jun Huh, Gloria Choi and colleagues provide a link between maternal infection, gut bacteria and the risk of developing behavioral and cortical abnormalities in mice.
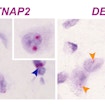
Christopher Gregg and colleagues demonstrate that diverse epigenetic mechanisms affect allele-specific gene expression in the mammalian brain.
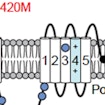
Kevin Bender and Stephan Sanders show that ASD-associated SCN2A variants lead to impaired NaV1.2 channel activity and reduced neuronal excitability.
Amiel Rosenkranz and colleagues have identified a specific intra-amygdala circuit, from the lateral nucleus to the medial nucleus, which is critical for social learning.
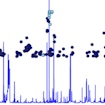
Lauren Weiss and colleagues used a reverse pathway genetic approach, focused on the RAS/MAPK pathway, to show that gene-gene interactions contribute to autism.
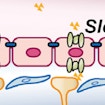
Gaia Novarino and Joseph Gleeson find impaired amino acid transport into brain causes ASD-like symptoms in mice, and uncover transport mutations in individuals with ASD.
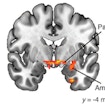
Suitable biomarkers are needed to assess treatment outcomes in ASD. Pamela Ventola has developed fMRI biomarkers that allow accurate prediction of intervention success.