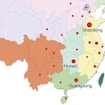
By assessing a Chinese autism cohort, Evan Eicher establishes the importance of de novo mutations for conferring autism risk in both European and Chinese populations.
Highlights of SFARI-funded papers, selected by the SFARI science team.

By assessing a Chinese autism cohort, Evan Eicher establishes the importance of de novo mutations for conferring autism risk in both European and Chinese populations.
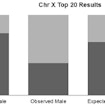
By examining SNPs from ASD datasets, Lauren Weiss finds that genetic mechanisms regulating general sex differences, such as height and weight, contribute to autism risk.
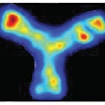
Betty Diamond reports on a method to isolate monoclonal brain-reactive antibodies from plasma obtained from mothers in the SSC, showing their in utero exposure can cause ASD.
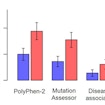
Using sequencing data from the Simons Simplex Collection, Zhenglong Gu found an enrichment of predicted pathogenic mutations in mitochondrial DNA in autism.
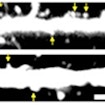
Benjamin Cheyette finds higher rates of DIXDCI disruptions in individuals with ASD, schizophrenia or bipolar, and DIXDC1 signaling rescue improves mouse ASD-like behaviors.
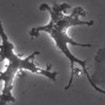
Rudolf Jaenisch has developed a method enabling the generation of microglia-like cells from human embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells.
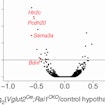
Liqun Luo uses conditional, cell-type-specific RAI1 deletions in mice to assess how loss of RAI1 contributes to neurodevelopmental phenotypes in Smith-Magenis syndrome.
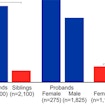
By assessing human accelerated regions (HARs) in healthy individuals and those with ASD, Chris Walsh shows HARs regulate human social and cognitive behavior and ASD risk.