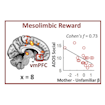
Vinod Menon and colleagues report that a difference in the activation of a voice-processing network comprising reward and salience detection systems is a distinguishing feature of autism.

Vinod Menon and colleagues report that a difference in the activation of a voice-processing network comprising reward and salience detection systems is a distinguishing feature of autism.

SFARI is pleased to announce that it has selected seven new clinical sites as a result of the 2019 SPARK Clinical Site Network request for applications. These sites will join the existing SPARK clinical site network and contribute to SPARK recruitment and engagement goals.
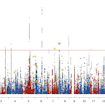
Mark Daly and colleagues report the results of a large genome-wide association meta-analysis of more than 18,000 individuals with ASD, including the newly genotyped Danish iPSYCH cohort.

Family-organized groups are planning a number of meetings in 2019 for individuals with rare genetic neurodevelopmental conditions, including those due to 16p11.2 copy number variants and mutations in ASXL3, CHAMP1, DYRK1A, HNRNPH2, PPP2R5D, SCN2A and STXBP1 single genes. SFARI can help facilitate research opportunities at these meetings by connecting investigators with families.

This issue of the SFARI newsletter includes: (1) Winter 2019 Pilot awardees announced, (2) Autism BrainNet begins distribution of new postmortem brain tissue, (3) SFARI Viewer has launched, (4) SFARI Gene: New data release, (5) Highlights of SFARI-funded research, (6) 2019 Novel Outcome Measures in ASD – Request for applications, (7) Summer 2019 Pilot Award – Request for applications.

SFARI Viewer, an online platform to visualize and analyze SFARI genomic data, was recently launched. This tool was developed through a collaboration between the SFARI Informatics team, Frameshift and the University of Utah, with the goal to facilitate data exploration and analysis from SFARI collections. These include the Simons Simplex Collection and SPARK.

Evan Eichler and colleagues performed a meta-analysis of de novo mutations from individuals with ASD, intellectual disability or developmental delay and found new risk genes for neurodevelopmental disorders.
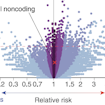
Stephan Sanders and colleagues used a machine learning approach to analyze whole-genome sequencing data from more than 1,900 SSC families and found that de novo noncoding variants in distal regions of promoters confer risk of ASD.
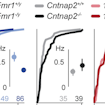
Dan Feldman and colleagues analyzed four mouse models of autism and found that alterations in the excitation-inhibition ratio may serve as a homeostatic mechanism to prevent network hyperexcitability.

SFARI is pleased to announce that it intends to fund 15 grants in response to the Winter 2019 Pilot Award request for applications (RFA).