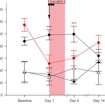
Irving Reti assesses, in two ASD mouse models, the utility of targeted, subthalamic nucleus, deep brain stimulation to treat severe forms of self-injurious behavior.

Irving Reti assesses, in two ASD mouse models, the utility of targeted, subthalamic nucleus, deep brain stimulation to treat severe forms of self-injurious behavior.
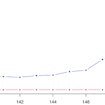
Evan Eichler compares whole-genome and whole exome sequencing data of ASD indivduals and finds an enrichment of variants in putative noncoding regulatory elements in ASD.

New collaboration will collect critically needed brain tissue for autism research

As an organization dedicated to the advancement of scientific knowledge, the Simons Foundation stands united with the scientists and institutions we support in their opposition to the recently announced executive order on visas and immigration to the United States from seven Middle Eastern countries.

Several studies have shown that a micro-duplication within 15q11-13 — a region on chromosome 15 — on the maternal chromosome is associated with autism. The duplicated region contains many genes, but UBE3A, which encodes a ubiquitin ligase, deserves special attention because duplications apparently restricted to the UBE3A gene have been found in people with autism.
On 5 February 2010, the Simons Foundation gathered a panel of experts to discuss what initially appears to be a surprising and unrelated pair of subjects: autism and fever. Anecdotal reports have found that fever can improve cognitive function and behavior in individuals with autism.

Much of the recent advances in autism have been on the genetic and behavioral levels of dysfunction present in the disorder. Comparatively little is known about altered function in the underlying neural circuitry. Aiming to generate discussion on the best avenues to pursue in order to better understand the circuitry in autism, SFARI on 17 May held a one-day workshop.
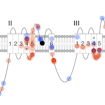
On August 2–3, 2019, people from around the world met in Seattle, Washington, to review recent findings about mutations to the sodium channel encoded by SCN2A. Organized by the FamilieSCN2A Foundation, the meeting hosted scientists as well as families of people affected by SCN2A mutations.

In this blog post, Paul Wang discusses the importance of supporting the development and validation of objective clinical outcome measures for autism. He also provides an overview of four new SFARI-funded projects that aim to develop such tools.

Steven Hyman discusses the use of disease model systems to study neuropsychiatric and neurodevelopmental conditions, highlighting their benefits and limitations, and stressing the importance of knowing what questions to address in each system.