

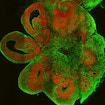
Two studies by different research groups — one led by Flora Vaccarino and the other by Juergen Knoblich — used brain organoids derived from pluripotent stem cells of people with autism and showed how transcriptional alterations affecting certain cell types during human brain development could contribute to the early emergence of ASD.
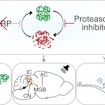
In a mouse model of fragile X syndrome, Emily Osterweil and her colleagues show that excessive protein synthesis drives a pathological compensatory rise in protein degradation (by the ubiquitin proteasome system), which can be targeted to correct various phenotypes including audiogenic seizures.

A study by Caroline Robertson and her colleagues found that reduced social attention was not a static omnipresent characteristic of autism; rather, it was magnified only under certain real-world conditions where sensory processing demands were high.