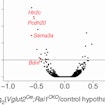
Copy number variants (CNVs) are segments of DNA that vary in copy number between different individuals. CNVs confer significant risk of neuropsychiatric disorders, including autism and schizophrenia. Notably, there appears to be a reciprocal relationship between copy number and brain size for certain genetic loci. For example, deletions of the genomic region 16p11.2 tend to be associated with autism and increased head circumference, whereas duplications of the same segment tend to be associated with schizophrenia and smaller head circumference. The contrasting clinical phenotypes that are associated with reciprocal changes in gene dosage could represent opposite extremes of the same neurodevelopmental process.